Bli med Paxi når han undersøker drivhuseffekten for å lære om global oppvarming.
★ Abonnere: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

See in this time-lapse how the Sentinel-3B satellite was prepared for its liftoff on 25 April 2018 from Plesetsk in Russia.
Sentinel-3B joined its twin, Sentinel-3A, in orbit. The pairing of identical satellites provides the best coverage and data delivery for Europe’s Copernicus programme – the largest environmental monitoring programme in the world. The satellites carry the same suite of cutting-edge instruments to measure oceans, land, ice and atmosphere.
Credits: Directed by Stephane Corvaja, ESA;
Edited by Manuel Pedoussaut, Zetapress;
Music by Hubrid-Rockot
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Watch the first set of images taken by Sentinel-3B http://bit.ly/FirstImagesSentinel3B

Astronomy is undergoing a revolution with the release of precision data on 1.7 billion stars in our galaxy from the Gaia space telescope. We head to the historic Observatory of Paris and ESA’s ESTEC base in the Netherlands to find out more.
It’s fair to say that science has been waiting for centuries, or even millennia for such a detailed survey of the Milky Way, and right now star-gazers are swamped with fresh, high-quality data that they can use to answer every question about the galaxy they ever wanted to ask.
This video is also available in the following languages:
German: https://youtu.be/I7EHdEnXGi4
French: https://youtu.be/dJRPGaS3VB4
Italian: https://youtu.be/hyOdUHRCDYA
Spanish: https://youtu.be/BCP4xg6sGeY
Portuguese: https://youtu.be/OeBMRQmojXc
Greek: https://youtu.be/Ra0BOhFJ4NU
Hungarian: https://youtu.be/-PYmrCk1iwM
★ Subscribe to our channel: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/GaiaRickestStarMap

Nesta edição de “Space”, a partir do Observatório de Paris, vamos encontrar-nos com astrónomos que trabalham numa missão especial do telescópio Gaia, que tem vigiado mais de mil milhões de estrelas da nossa galáxia, tentando dar resposta a alguns dos mistérios da Via Láctea.
★ Inscreva-se no nosso canal: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

This movie, based on images taken by ESA’s Mars Express, showcases the 102 km wide Neukum Crater in the southern hemisphere of Mars.
The crater is named for the German physicist and planetary scientist, Gerhard Neukum, one of the founders of ESA’s Mars Express mission who inspired and led the development of the high-resolution stereo camera on Mars Express.
This complex impact crater has a diverse geologic history, as indicated by various features on the crater rim and floor. Particularly striking are the dark dune fields, likely made up of volcanic material blown in and shaped by strong winds.
The crater’s shallow interior has been infilled by sediments over its history. It is also marked with two irregular depressions that may be a sign of a weaker material that has since eroded away, leaving behind some islands of more resistant material.
Over time the crater rim has undergone varying degrees of collapse, with landslides and slumped material visible in the crater walls. Many smaller craters have also overprinted the rim and pockmarked the interior since Neukum Crater was formed, highlighting its long history.
Neukum Crater is situated in Noachis Terra, one of the oldest known regions on Mars, dating back to at least 3.9 billion years.
Credits: Animation: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO; Music: Coldnoise, CC BY-SA 4.0 and Adrian Neesemann
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/ESACraterNeukum

‘Horizons’ is the name of ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst’s second mission to the International Space Station.
The mission name evokes exploring our Universe, looking far beyond our planet and broadening our knowledge. Alexander would also like to make people realise that there is always a chance to go beyond their personal horizons.
Alexander will be launched on 6 June with US astronaut Serena Auñón-Chancellor and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Prokopyev from the Baikonur cosmodrome, Kazakhstan in the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft.
Alexander will take over command of the International Space Station for the second half of his mission. Alexander Gerst is the 11th German citizen to fly into space.
The astronaut is now in the last stages of training for his challenging spaceflight. The science programme is packed with European research: more than 50 experiments will deliver benefits to people back on Earth and prepare for future space exploration.
Credits: ESA
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/HorizonsOverview

Spacecraft in orbit and on Mars’s surface have made many exciting discoveries, transforming our understanding of the planet and unveiling clues to the formation of our Solar System, as well as helping us understand our home planet. The next step is to bring samples to Earth for detailed analysis in sophisticated laboratories where results can be verified independently and samples can be reanalysed as laboratory techniques continue to improve.
Bringing Mars to Earth is no simple undertaking—it would require at least three missions from Earth and one never-been-done-before rocket launch from Mars.
A first mission, NASA’s 2020 Mars Rover, is set to collect surface samples in pen-sized canisters as it explores the Red Planet. Up to 31 canisters will be filled and readied for a later pickup – geocaching gone interplanetary.
In the same period, ESA’s ExoMars rover, which is also set to land on Mars in 2021, will be drilling up to two meters below the surface to search for evidence of life.
A second mission with a small fetch rover would land nearby and retrieve the samples in a Martian search-and-rescue operation. This rover would bring the samples back to its lander and place them in a Mars Ascent Vehicle – a small rocket to launch the football-sized container into Mars orbit.
A third launch from Earth would provide a spacecraft sent to orbit Mars and rendezvous with the sample containers. Once the samples are safely collected and loaded into an Earth entry vehicle, the spacecraft would return to Earth, release the vehicle to land in the United States, where the samples will be retrieved and placed in quarantine for detailed analysis by a team of international scientists.
Credits: NASA/ESA
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/BringingMartianSoilToEarth

Roundup from ESA WebTV of Day 3 at the Berlin Air and Space Show, 27 April
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/ESAAtILA

Roundup of Day 2 at the Berlin Air and Space Show, 26 April
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: bit.ly/ESAAtILA

Earth from Space is presented by Kelsea Brennan-Wessels from the ESA Web TV virtual studios. A mosaic of cloud-free images from the Copernicus Sentinel-3A satellite spanning Europe is featured in this edition.
See also http://www.esa.int/spaceinimages/Images/2018/04/Cloud-free_Europe to download the image.
Image acquired by Sentinel-3
Animation credits: ATG medialab
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

The Copernicus Sentinel-3B satellite spent six weeks at the Plesetsk cosmodrome in Russia being carefully prepared for liftoff. After being shipped from France to the launch site, the satellite was tested, joined to the rocket launch adapter, sealed from view in the fairing and taken by train to the launch pad. Sentinel-3B lifted off on 25 April 2018 at 17:57 GMT (19:57 CEST).
It joins its twin, Sentinel-3A, in orbit. The pairing of identical satellites provides the best coverage and data delivery for Europe’s Copernicus programme – the largest environmental monitoring programme in the world. The satellites carry the same suite of cutting-edge instruments to measure oceans, land, ice and atmosphere. While these data are fed primarily into the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service, all the Copernicus services benefit to produce knowledge and information products in near-real time for a wide range of applications. The Sentinel-3 mission is essential for applications for ocean and coastal monitoring, numerical weather and ocean prediction, sea-level change and sea-surface topography monitoring, ocean primary production estimation and land-cover change mapping.
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

The second data release of ESA’s Gaia mission has produced an extraordinary catalogue of over one and a half billion stars in our galaxy. Based on observations between July 2014 to May 2016, it includes the most accurate information yet on the positions, brightness, distance, motion, colour and temperature of stars in the Milky Way as well as information on asteroids and quasars.
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/GaiaRickestStarMap

Animated 3D view of the sky as observed by ESA’s Gaia satellite using information from the mission’s second data release.
The bright band in the left half of the image is the Milky Way, where most of the stars in our Galaxy reside. The animation starts with the Orion constellation at the centre; we then move towards the neighbouring Taurus constellation and to the Hyades star cluster, which is part of this constellation. Hyades is the closest open cluster to the Solar System, some 150 light-years away.
The animation first shows the 3D structure of the cluster, based on accurate position and distance information from Gaia. Then an animated view of the future motions of stars is shown – both in Hyades and beyond. This is based on Gaia’s measurements of the velocity of stars across the sky, also known as proper motion.
Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC, CC BY SA 3.0 IGO
Acknowledgement: Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium (DPAC); Gaia Sky; S. Jordan / T. Sagristà, Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg, Germany
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: bit.ly/GaiaRickestStarMap

Animated view of 14 099 asteroids in our Solar System, as viewed by ESA’s Gaia satellite using information from the mission’s second data release. The orbits of the 200 brightest asteroids are also shown, as determined using Gaia data.
In future data releases, Gaia will also provide asteroid spectra and enable a complete characterisation of the asteroid belt. The combination of dynamical and physical information that is being collected by Gaia provides an unprecedented opportunity to improve our understanding of the origin and the evolution of the Solar System.
Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC, CC BY SA 3.0 IGO
Acknowledgement: Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium (DPAC); Orbits: Gaia Coordinating Unit 4; P. Tanga, Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur, France; F. Spoto, IMCCE, Observatoire de Paris, France; Animation: Gaia Sky; S. Jordan / T. Sagristà, Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg, Germany
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: bit.ly/GaiaRickestStarMap

A 360° animated view of the entire sky on 25 April 2018.
After a few seconds, the stars start moving in the sky according to parallax, an apparent shift caused by Earth’s yearly motion around the Sun. Then, constellation outlines appear as visual aids. Finally, stars start moving according to their true motion through space, which is visible on the sky as proper motion. Parallaxes have been exaggerated by 100 000 and proper motions have been speeded up by one trillion (10^12) to make them visible in this animation. This animation is based on data from the second data release of ESA’s Gaia satellite, which has measured the positions, parallaxes and motions of more than one billion stars across the sky to unprecedented accuracy.
ESA/Gaia/DPAC, CC BY SA 3.0 IGO
Acknowledgement: Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium (DPAC); Gaia Sky; S. Jordan / T. Sagristà, Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg, Germany
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Learn more: http://bit.ly/GaiaRickestStarMap

Meet our new space explorers, the spacecraft of the BepiColombo mission, as they begin their adventure to planet Mercury. But first, they have to navigate through Amsterdam Schiphol airport to reach Europe’s spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana.
The spacecraft really do depart from Schiphol; along with essential ground-support equipment they are scheduled to fly in a series of Antonov aircraft during the last week of April and first week of May. Upon arrival at Kourou, an intensive six-months of preparations will prepare the mission for launch. The launch window opens 5 October until 29 November 2018.
Find out more about the BepiColombo mission on esa.int/bepicolombo
Credits: ESA
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe
Follow Bepi: http://bit.ly/BepiTwitter
Follow MMO: http://bit.ly/MMOTwitter
Follow MTM: http://bit.ly/MTMtwitterESA

On 25 April 2018, ESA’s Gaia mission will publish its much awaited second data release, including high-precision measurements of nearly 1.7 billion stars in our Galaxy.
Scientists who have been working on creating and validating the data contained in the catalogue tell us why they are waiting for this extraordinary release.
Featured in the video: Antonella Vallenari (INAF, Astronomical Observatory of Padua), Anthony Brown (Leiden University), Timo Prusti (European Space Agency), Annie Robin (Institut UTINAM, OSU THETA Franche-Comté-Bourgogne), Laurent Eyer (University of Geneva) and Federica Spoto (IMCCE, Observatory of Paris).
A media briefing on the second Gaia data release will be held at the ILA Berlin Air and Space Show in Germany on 25 April 11:00-12:15 CEST. Watch the webstream at www.esa.int/live
Learn more about Gaia: bit.ly/ESAsGaia
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

We meet a surfing scientist and toxic algae hunters to see how Sentinel-3 satellite data is used to study the coastline of the English Channel in this month’s episode of Space.
Bob Brewin is pioneering a new technique in satellite oceanography – by going surfing.
The Plymouth Marine Laboratory scientist uses his board to take sea surface temperature measurements, and then use them to better interpret data from European satellite Sentinel-3.
This video is also available in the following languages:
German: https://youtu.be/1dU52RA1IEE
French: https://youtu.be/kSJXmrSWG-s
Italian: https://youtu.be/PRPvcvZgQno
Spanish: https://youtu.be/H0vQdyanyKk
Portuguese: https://youtu.be/_nP6Bmpa6YQ
Greek: https://youtu.be/y4zObvFjckY
Hungarian: https://youtu.be/kj3-iO2S4UQ
★ Subscribe to the channel: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

In this special edition of Earth from Space, senior project scientist at Gamma Remote Sensing, Dr Maurizio Santoro, joins the show to discuss how his team estimates forest biomass from space.
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe

Our alien friend Paxi, ESA Education’s mascot, went to visit American astronaut Scott Tingle on board the International Space Station. Tingle tells Paxi about how astronauts sleep in weightlessness, an important aspect of living on the ISS.
Credit: ESA/NASA
#ESA
#Paxi
#InternationalSpaceStation

Having a stressful day? We got you covered! Sit back, turn the volume up and enjoy a relaxing moment brought to you by ESA and Lufthansa exploring the countries which make up the European Space Agency with images taken by the Copernicus Sentinel-1A, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-3A, Proba-V and Envisat satellites.
Don’t forget to favourite this video. You will always have a space to relax with us.
Music by Matt Baute.

Every week, on average, a substantial, inert satellite drops into our atmosphere and burns up. Monitoring these reentries and warning European civil authorities has become routine work for ESA’s space debris experts.
Each year, about 100 tonnes of defunct satellites, uncontrolled spacecraft, spent upper stages and discarded items like instrument covers are dragged down by Earth’s upper atmosphere, ending their lives in flaming arcs across the sky.
Some of these objects are big and chunky, and pieces of them survive the fiery reentry to reach the surface. Our planet, however, is a big place, mostly covered by water, and much of what falls down is never seen by anyone, sinking to the bottom of some ocean, or landing far from human habitation.
While still in orbit, these and many other objects are tracked by a US military radar network, which shares the data with ESA, since Europe has no such capability of its own.It’s the task of ESA’s Space Debris team to look at these data and issue updates to ESA Member States and partner civil authorities around the globe.
Visit http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Operations/Space_Debris/ESA_reentry_expertise to learn more

The video features footage taken of the parachute deployment as seen from the ground, as well as from onboard GoPros fixed to the drop test vehicle and looking up at the parachute. The test focused on the deployment and inflation of the second main stage 35m-wide parachute, which will be the largest to fly on Mars.
Discussing the test are Stephane Langlois, ESA ExoMars engineer, and John Underwood, principal engineer at Vorticity.
The test was carried out by Vorticity Ltd under supervision of Thales Alenia Space France, Thales Alenia Space Italy and ESA, in Kiruna, Sweden, on 2 March 2018.
Credits: ESA & Vorticity Ltd

Having a stressful day? We got you covered!Sit back, turn the volume up and enjoy a relaxing moment brought to you by ESA and Lufthansa getting lost in the beauty of our planet with images captured by Envisat, JAXA ALOS, KARI Kompsat-2, GeoEye Ikonos-2 and NASA Landsat-5 and Landsat-7 satellites.
Don’t forget to favourite this video. You will always have a space to relax with us.
Music: “Page of Life” by Green Sun.

Earth from Space is presented by Kelsea Brennan-Wessels from the ESA Web TV virtual studios. In this edition, Sentinel-2A satellite takes us over Japan’s capital, the world’s largest megacity.
See also http://www.esa.int/spaceinimages/Images/2018/03/Tokyo to download the image.

Having a stressful day? We got you covered! Sit back, turn the volume up and enjoy a relaxing moment brought to you by ESA and Lufthansa exploring the coldest parts of our planet with a collection of ice images captured by the Envisat satellite.
Don’t forget to favourite this video. You will always have a space to relax with us.
Music: “Page of Life” by Green Sun.

These observations of Phobos and Saturn were taken by the Super Resolution Channel of the High Resolution Stereo Camera on Mars Express. The video comprises 30 separate images acquired during Mars Express orbit 16 346 on 26 November 2016. The slight up and down movement of Saturn and Phobos in these images is caused by the oscillation of the spacecraft’s orientation after completing the turn towards the moon. Phobos can be seen in the foreground, partially illuminated, with Saturn visible as a small ringed dot in the distance.
For more information go tohttp://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/Mars_Express/Mars_Express_views_moons_set_against_Saturn_s_rings

A dél-spanyolországi Rio Tinto nevű hely gyakorlatilag a Mars a Földön. Ha itt van élet, vajon lehet a vörös bolygón is?

A Euronews esteve em Huelva, onde conheceu o Rio Tinto, cujas margens e sedimentos se parecem em todos os aspetos aos do Planeta Vermelho.
Um grupo de cientistas procura sinais de vida noutros planetas do nosso sistema solar. E fazem-no com a recolha de amostras dos lugares mais inesperados.

The Rio Tinto river snakes through the Spanish countryside for 100 kilometres, a dark, blood-red stain of acid water and rusty-looking rocks that scientists love to study. Both ESA and NASA experts regularly spend weeks in the Rio Tinto, examining the life underground, and using it as a test bed to look for life on Mars.
This video is also available in the following languages:
German: https://youtu.be/K2D8T5i_Myk
French: https://youtu.be/7cynIaX5O0I
Italian: https://youtu.be/LOYgvHSR84g
Spanish: https://youtu.be/YI9Prr0ZVrw
Portuguese: https://youtu.be/VSDmRn-rRTE
Greek: https://youtu.be/7KW2SJc2Yjo
Hungarian: https://youtu.be/M0c6Ev63acs

Since arriving at Mars in October 2016, the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter has been aerobraking its way into a close orbit of the Red Planet by using the top of the atmosphere to create drag and slow down. It is almost in the right orbit to begin observations – only a few hundred kilometres to go! With aerobraking complete, additional manoeuvres will bring the craft into a near-circular two-hour orbit, about 400 km above the planet, by the end of April. The mission’s main goal is to take a detailed inventory of the atmosphere, sniffing out gases like methane, which may be an indicator of active geological or biological activity. The camera will help to identify surface features that may be related to gas emissions. The spacecraft will also look for water-ice hidden below the surface, which could influence the choice of landing sites for future exploration. It will also relay large volumes of science data from NASA’s rovers on the surface back to Earth and from the ESA–Roscosmos ExoMars rover, which is planned for launch in 2020.
Visit our website to learn more about ExoMars: https://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/ExoMars

Ginevra Favole is an ESAC research fellow working on the large-scale structures of the universe. Her main scientific field is emission-line galaxies, galaxy clustering and weak gravitational lensing. She also works with mock catalogues and N-body cosmological simulations.
Go to https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/esac-science-faculty/home to learn more.

Maggie Lieu is an ESAC research fellow working on Euclid, a visible and near-infrared space telescope due to launch in 2021. By measuring the shapes of distant galaxies we can determine the mass of the largest systems in the Universe, galaxy clusters. Euclid will achieve unprecedented shape measurements of galaxies covering almost half of the extragalactic sky.Maggie is developing statistical methods to deal with this upcoming big, noisy dataset, so that we can better understand the physics of galaxy clusters and theirrolein the Dark Universe.
Go to https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/esac-science-faculty/home to learn more.

Looking at a decade of European science on the International Space Station with the Columbus laboratory.
Columbus houses as many disciplines as possible in a small volume, from astrobiology to solar science through metallurgy and psychology – more than 227 experiments have been carried out during this remarkable decade. Countless papers have been published drawing conclusions from experiments performed in Columbus.
From circadian rhythms and new temperature sensors to edible algae as astronaut food through running experiments to grow crystals and investigate processes in a pure environment without gravity interfering with the process – Columbus helping scientists push the boundaries of what is possible and increase our knowledge for life on Earth.
More about Columbus:
http://www.esa.int/columbus

The Moon is a destination, a laboratory for science, a place to learn the skills of planetary exploration, and a source of materials and energy for use on the Moon and in space to create new spacefaring capability.
Advocate of a human return on the Moon, Paul D. Spudis, Senior Staff Scientist at the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston (Texas, USA), takes us on a journey to rediscover the value of lunar exploration, a topic on which he has spent more than 40 years of study, thought and publications.
Space Bites hosts the best talks on space exploration from the most inspiring and knowledgeable speakers from the field. Held at the technical heart of the European Space Agency in the Netherlands, the lectures are now also available on YouTube. If you want to know about the present and future challenges of ESA, stay tuned for more.
To know more about the exploration of the Moon visit http://lunarexploration.esa.int
★ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/ESAsubscribe and click twice on the bell button to receive our notifications.
Check out our full video catalog: http://bit.ly/SpaceInVideos
Follow us on Twitter: http://bit.ly/ESAonTwitter
On Facebook: http://bit.ly/ESAonFacebook
On Instagram: http://bit.ly/ESAonInstagram
On Pinterest: https://bit.ly/ESAonPinterest
On Flickr: http://bit.ly/ESAonFlickr
We are Europe’s gateway to space. Our mission is to shape the development of Europe’s space capability and ensure that investment in space continues to deliver benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world. Check out https://www.esa.int/ to get up to speed on everything space related.
Copyright information about our videos is available here: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Terms_and_Conditions
#ESA
#SpaceBites
#LunarExploration
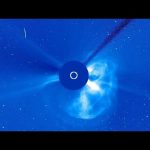
The Sun unleashed powerful solar flares on 6 September, one of which was the strongest in over a decade. An X2.2-class flare was launched at 09:10 GMT and an X9.3 flare was observed at 12:02 GMT. An M-class flare was also observed two days earlier on 4 September.
The images were captured by the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, SOHO. The flares were launched from a group of sunspots classified as active region 2673.The shaded disc at the centre of the image is a mask in SOHO’s LASCO instrument that blocks out direct sunlight to allow study of the faint details in the Sun’s corona. The white circle added within the disc shows the size and position of the visible Sun.
More about SOHO:
http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/SOHO_overview2
Credit: SOHO (ESA & NASA)

The LISA Pathfinder mission ends on 18 July 2017 after a successful demonstration of the technology needed to detect gravitational waves in space. These vibrations in spacetime, first predicted by Einstein over a hundred years ago, are produced by huge astronomical events – such as two black holes colliding – and will allow scientists to open new windows into our universe.
The success of the LISA Pathfinder mission has paved the way for the newly selected LISA mission which, when built and launched, will detect gravitational waves from objects up to a million times larger than our Sun.
The film features interview soundbites from Dr Paul McNamara, LISA Pathfinder Project Scientist, at the European Space Agency’s European Technology and Science facility (ESTEC) in The Netherlands.
More about LISA Pathfinder:
http://sci.esa.int/lisa-pathfinder/
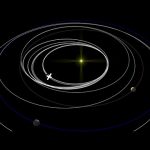
Animation visualising BepiColombo’s 7.2 year journey to Mercury.
This animation is based on a launch date of 5 October, marking the start of the launch window in October 2018. It illustrates the gravity assist flybys that the spacecraft will make at Earth, Venus and Mercury before arriving at Mercury in December 2025.
More about the journey:
http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/BepiColombo/Journey_to_Mercury