President Obama’s FY2014 budget request for NASA enables the agency to leverage capabilities in the Human Exploration and Operations, Science and Space Technology Mission Directorates to make significant yet affordable advances in our nation’s capabilities and achieve the space goals set by the Administration. NASA will improve detection and characterization of asteroids, pursue solar electric propulsion demonstration, develop a mechanism to capture an asteroid and redirect it to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system and begin designing a mission to send humans to it using the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
Author: kidibot
-
Magic Tube – Sick Science! #134
Tissue paper is known for a few things. For example, tissue paper is soft and nice for blowing your nose. Tissue paper is not, however, known for its tensile strength. Most people wouldn’t be surprised if a common housefly could tear through a piece. In the Magic Tube – Strong Tissue Paper experiment, though, we’ll show you a way to make tissue paper nearly impenetrable.
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Inc. all rights reserved
-

NASA Celebrates Earth Month 2013: NASA Science Eyes
NASA’s fleet of science satellites and research aircraft are at work around the world 24/7 helping scientists discover just how our living planet really works. Take a look at some of the insights and don’t forget to celebrate Earth Day on April 22!
-

NASA Celebrates Earth Month 2013: The View from Orbit
Take a look at the beauty and wonder of our home planet as seen from space by astronauts on the International Space Station. And don’t forget to celebrate Earth Day on April 22!
-

CanSat video
Sequences extracted from the 2012 European competition campaign at Andøya Rocket Range in Norway.
-

Micha Schmidt and Elsa Montagnon talk about their careers at ESA
Micha Schmidt is a Spacecraft Operations Manager at ESA. In this video he talks about his involvement in the Herschel project and the many phases of development that exist in all ESA projects. Micha also talks about his fascination for space as a boy and what a great experience it has been to live in various European countries whilst working for ESA.
Elsa Montagnon is a Spacecraft Operations Manager for the BepiColombo project. Still in the development phase, BepiColombo should be launched in 2015 and hopes to provide more information about Mercury than ever before. In this video Elsa discusses her involvement in the mission, her studies and hobbies, as well as the passion people have at ESA for their projects.
-

Introduction to the International Space Apps Challenge by ESA Astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti
The International Space Apps Challenge (http://spaceappschallenge.org) is a global collaboration of space explorers, held in cities around the world on April 20-21, 2013. In the style of a hackathon, citizen experts will collaborate with space agencies and other partners to further space technology, as well as use space data to solve Earth-bound challenges. Join us on Earth Day weekend!
-

First Light for AMS on This Week @ NASA…
Researchers have published the first findings of the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), a particle physics detector on the International Space Station that searches for various types of unusual cosmic matter. Scientists hope that by measuring cosmic rays, AMS will provide new data about the formation of the Universe, antimatter, and evidence of the mysterious dark matter believed to make up most of the Universe. Also, MATERIALS IN SPACE, OBSERVING EARTH, FARTHEST SUPERNOVA YET, BLOWING IN THE WIND, EARTH MONTH 2013 and more!
-

NASA Engineer Shares Software Smarts
Students on NASA’s Digital Learning Network hear from NASA’s Megan Hashier about her role as software Engineer for the International Space Station. Host: Kyle Herring.
-

ESTEC Shake
This version of the “Harlem Shake” video, called the “ESTEC Shake”, was filmed on a real ‘electrodynamic shaker’, normally used to test spacecraft at the European Space Agency’s technical centre, ESTEC, in Noordwijk, the Netherlands. One of the major risks faced by satellites stems from the high vibrations they experience during launch. It is essential to test spacecraft and their components under similar conditions on such shakers to make sure they will survive the violent ride into space.
ESA’s Test Centre is the largest centre of its kind in Europe, and one of the largest in the world.The video was filmed by ESTEC volunteers, in their own time, at zero cost, while the shaker unit was being reconfigured. Strict safety, security and cleanroom procedures were followed during filming.
More about ESA’s ESTEC Test Centre
http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Engineering/About_ESTEC_Test_Centre2More about the “Shaker”
http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Engineering/Electrodynamic_shakersMusic: “Harlem Shake”, by Baauer (Mad Decent), www.maddecent.com
-

Make Your Own Lightsaber – Sick Science! #137
From Tatooine to Hoth, there is one legendary weapon that is regarded as the ultimate in Rebel and Empire warfare… the lightsaber. Ewoks, Wookies, Jawas, and droids all cower before the mighty lightsaber. Wanna make your own? Let us take you to a galaxy far, far away and teach you how you can build your own working lightsaber. Trust us, it works.
Want to build your own lightsaber? Buy the items needed here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/energy-modulation-circuit
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Inc all rights reserved
About Steve Spangler…
Steve Spangler is a celebrity teacher, science toy designer, speaker, author and an Emmy award-winning television personality. Spangler is probably best known for his Mentos and Diet Coke geyser experiment that went viral in. Spangler is the founder of www.SteveSpanglerScience.com, a Denver-based company specializing in the creation of science toys, classroom science demonstrations, teacher resources and home for Spangler’s popular science experiment archive and video collection. Spangler is a frequent guest on the Ellen DeGeneres Show and Denver 9 News where he takes classroom science experiments to the extreme. For teachers, parents or DIY Science ideas – check out other sources of learning:
Join the Science Club and check out other cool science experiments at – http://www.SteveSpanglerScience.com
Sign up to receive a FREE Experiment of the Week- http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment-of-the-week
Attend a Spangler Hands-on Science Workshop for Teachers – http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/training
Watch Steve on Local and National Media Appearances on YouTube at: https://www.youtube.com/user/SpanglerScienceTV
-

All Aboard for Cassidy and Crewmates on This Week @NASA
NASA Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy and his Expedition 35/36 crewmates, Soyuz Commander Pavel Vinogradov, and Russian Flight Engineer Alexander Misurkin, are now safely aboard the International Space Station, where they’ll conduct scientific research through the summer. Also, Dragon’s back; Heatshield Hits Beantown; Stir Welding for SLS; Cassini Hot Spots; Hangout En Espanol; and more!
-

Impossible Egg Crush – Sick Science! #133
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-
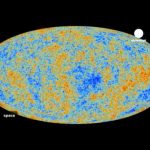
ESA Euronews: Planck maps the dawn of time
Scientists have traced a unique new map of the first light of the universe, and raised profound questions about the Big Bang.The image of the cosmic microwave background they have released was taken by ESA’s Planck satellite, and its results could have a significant impact on the field of cosmology.
“It turns that most of this image, most of this map, fits beautifully our very simple model. At the same time we find some strange things, and this is where it starts to get interesting, because we see some signs of things that do not fit,” explains ESA’s Planck Project Scientist Jan Tauber.
“Roughly speaking the things that we are finding that are not as we expect are features that are across the whole sky. When you look only at the large features on this map you find that that our best fitting model, our best theory has a problem fitting the data, there is a lack of signal that we would expect to see,” he says.
The news that the early universe is not quite as was thought has left the greatest minds in cosmology spinning with excitement.
George Efstathiou, Professor of Astrophysics, University of Cambridge, is a key member of the Planck Science Team.
“The idea that you can actually experimentally test what happened at the Big Bang still amazes me,” he says.
The Big Bang theory remains intact of course, but the concept of inflation could be put to test by the Planck data.
“We see these strange patterns that are not expected in inflationary theory, the simplest inflationary theories,” explains Efstathiou.
“So there’s a real possibility that we have an incomplete picture. It may be that we have been fooled, that inflation didn’t happen. It’s perfectly possible that there was some phase of the universe before the Big Bang actually happened where you can track the history of the universe to a pre-Big Bang period.”
The Planck mission could test ideas about how the early universe was formed.The puzzle is that at small scales the data fits the theoretical model very nicely, but at larger scales the signal from the cosmic microwave background is much weaker than expected.
Efstathiou is looking for answers: “Can we find a theoretical explanation that links together the different phenomena that we have seen, the different little discrepancies, with inflationary theory? That’s where there’s the potential for a paradigm shift, because at the moment there’s no obvious theoretical explanation that links together these anomalies that we have seen. But if you found a theory that links phenomena that were previously unrelated, then that’s a pointer to new physics.”
It appears that the audacious Planck mission really will shed new light on the dawn of time.
-

Planck reveals an almost perfect Universe
Acquired by ESA’s Planck space telescope, the most detailed map ever created of the cosmic microwave background — the relic radiation from the Big Bang — was released today, revealing the existence of features that challenge the foundations of our current understanding of the Universe.
-

Growing and Shrinking Marshmallows #132
Find out why the Peeps expand here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment/growing-marshmallows
A vacuum packer is an amazing device that vacuum packs food to seal in the freshness. At least that’s what those late night infomercials tell us. We’re more excited about using this fascinating device to explore amazing scientific properties. Fill the special storage container with marshmallows (we prefer those adorable yellow Peeps) and watch the incredible growing marshmallow trick!
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Inc. all rights reserved
-

Marshburn’s Space Mash-up with 30 Seconds to Mars
Aboard the International Space Station, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA discussed his mission, research activities and answered social media questions offered by lead singer Jared Leto of the musical rock group “30 Seconds to Mars” during a tour of Mission Control, Houston by the group March 18. The members of the Los Angeles-based group, which was originally formed in 1998, are huge space enthusiasts, and recently had a sample of their music flown to the station on the SpaceX/Dragon cargo ship for the crew’s listening pleasure.
-

Mars Once Habitable on This Week @NASA
Analysis of the first ever sample of rock powder collected by the Mars Curiosity rover has proven that the Red Planet location it’s exploring once had everything needed to support microbial life including a lakebed filled with not salty or acidic but fresh water. Also, innovative space technology; students help space exploration; women aspiring, inspiring; IceBridge preps; SLS @ TennTech; career day; and more!
-

NASA Mars Curiosity Rover Report — March 15, 2013
A NASA Mars Curiosity rover team member gives an update on developments and status of the planetary exploration mission. The Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft delivered Curiosity to its target area on Mars at 1:31:45 a.m. EDT on Aug. 6, 2012 which includes the 13.8 minutes needed for confirmation of the touchdown to be radioed to Earth at the speed of light. The rover will conduct a nearly two-year prime mission to investigate whether the Gale Crater region of Mars ever offered conditions favorable for microbial life.
Curiosity carries 10 science instruments with a total mass 15 times as large as the science payloads on NASA’s Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity. Some of the tools, such as a laser-firing instrument for checking rocks’ elemental composition from a distance, are the first of their kind on Mars. Curiosity will use a drill and scoop, which are located at the end of its robotic arm, to gather soil and powdered samples of rock interiors, then sieve and parcel out these samples into the rover’s analytical laboratory instruments.
-

Dancing Spaghetti – Sick Science! #131
Unlock the mystery here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment/dancing-noodles
Who taught these noodles to dance, anyway? Go on – gather up some pasta noodles, turn up the music, and get ready for an old-fashioned pasta party. Just when you thought you were done at the dinner table… here is some kitchen science that will have you learning about volume and density in a brand new, hands-on way!
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-

Luca Parmitano Training
In less than three years, Luca has travelled between all five international partners’ training sites, gaining the knowledge and skills required for his mission. His tailored training has taken him to Houston, USA, Star City near Moscow, Russia, Tsukuba near Tokyo, Japan, Montreal, Canada, and the European Astronaut Centre in Cologne, Germany.
Critical tasks are trained over and over. As Soyuz flight engineer, Luca requires a great amount of ‘flying hours’ in the Russian spacecraft simulator, so he trained until he felt at home in the cockpit and can operate Soyuz flawlessly in any situation. During simulations, Luca had his hands at the controls of the spacecraft and wore the Russian Sokol flight suit.
Luca has been taught Space Station systems in full-size mockups, where he familiarised himself with the Station and learnt how everything works. He is trained in all systems and experiment operations scheduled for his mission. He has spent hours getting to know every corner of Europe’s Columbus laboratory, where most of the experiments in which he participates in take place.
Dressed in a spacesuit, Luca also trained to perform spacewalks in one of the largest swimming pools in the world on realistic mockups of the Space Station. -

Magic Spheres – Sick Science! #130
Discover the secret here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/content/experiment/magic-spheres
“For this trick, all you need is a bit of un-popped pop corn and a ball bearing.” It’s the perfect phrase to get all of the people around you excited for a bit of science magic. Many people don’t realize that pop corn and ball bearings have a remarkable chemical reaction that turns the ball bearing into a ping pong ball. In fact, when you perform the demonstration, your audience won’t believe their eyes.
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-

NASA’s Van Allen Probes Discover Third Belt Around Earth
In a briefing held Feb. 28 at the Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory, scientists detail the finding by NASA’s Van Allen Probes of a previously-undetected third radiation belt around Earth.
-

Static Flyer – Sick Science! #129
Read the full experiment here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment/static-flyer-flying-bag
Who needs a magic wand to create levitating objects when you have a balloon? In the Static Flyer experiment, we’ll teach you how understanding certain scientific ideas can result in a trick that would make Harry Potter, Gandalf the Grey, and even Merlin jealous.
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-

Anne Pacros: Payload system engineer
Academic background series: Anne Pacros is a payload system engineer on the Solar Orbiter mission and finds working in a position where all the threads of the project come together fascinating.
-

ESA Euronews: Η έλξη της βαρύτητας στη γη
Η βαρύτητα είναι μία θεμελιώδης δύναμη της φύσης, μία αόρατη έλξη που κυβερνά τον πλανήτη, κι αυτό την κάνει ζωτικής σημασίας. Μπορεί να μεταβάλλεται στο χρόνο λόγω της κίνησης της μάζας αλλά και να διαφοροποιείται από τόπο σε τόπο. Πρόκειται για ένα πραγματικό παζλ για τους επιστήμονες.
Η τιμή της βαρύτητας σε ένα μέρος μπορεί να εναλλάσσεται εξαιτίας της παλίρροιας. “Η δράση του φεγγαριού και του ήλιου αλλάζει το πεδίο βαρύτητας και η γη ανταποκρίνεται με ελαστικότητα σε αυτές τις αλλαγές και παραμορφώνεται”, λέει η ειδικός Κάρλα Μπρέιτενμπουργκ. Έτσι, εάν σαρώσει κανείς την γη με έναν ειδικό δορυφόρο για την βαρύτητα, το σχήμα της μοιάζει πραγματικά περίεργο.
“Εδώ και 20 χρόνια θα έλεγα ότι οι επιστήμονες ονειρεύονται μία αποστολή που να προσφέρει υψηλής ποιότητας ανάλυση της βαρύτητας”, τονίζει ο Βόλκερ Λίμπεγκ, διευθυντής του Προγράμματος Εξερεύνησης της γης της ESA.
Ο μόνος τρόπος για να έχουμε μία συνολική εικόνα του πεδίου βαρύτητας είναι να βρεθούμε στο διάστημα, κι αυτό ακριβώς κάνει η ESA με τους δύο δορυφόρους GRACE ανίχνευσης βαρύτητας. Με τα στοιχεία που μεταδίδουν, ειδικοί μπορούν να ανιχνεύσουν την δομή και την ιστορία της γης, ενώ μπορούμε να παρακολουθήσουμε και τις κλιματικές αλλαγές.
“Η μεγάλη καινοτομία του ανιχνευτή βαρύτητας είναι ότι για πρώτη φορά μπορούμε να έχουμε ένα καθολικό πεδίο που έχει την ακρίβεια και την ανάλυση που μας επιτρέπει να εντοπίζουμε τις αλλαγές της μάζας που συνδέονται με την γεωλογική δομή”, αναφέρει η Κάρλα Μπρέιτενμπουργκ.
Η κληρονομιά της αποστολής είναι μία άνευ προηγουμένου σφαιρική έρευνα για την βαρύτητα και την Γη.
-

Ready the Dragon on This Week @NASA
March 1st is the targeted launch date for the next cargo resupply flight to the International Space Station. Liftoff of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft’s second resupply mission to the ISS is scheduled for 10:10 a.m. Eastern from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Dragon will be loaded with about six tons of crew supplies and materials for science research. Also, Launch the Seedlings!; Curiosity Drills; ISS Social; Hangout with the Crew; Bolden Honored; Aerospace Days; Cady and the Chieftains; and more!
-

Space Station Hosts First Hangout
Aboard the International Space Station, Expedition 34 Commander Kevin Ford of NASA, Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA and Flight Engineer Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency fielded questions from social media during a Google Plus hangout February 22, the first for the station. The three astronauts answered questions from the online community who have been interested to watch and ask questions to astronauts both on orbit and on the ground. People from around the world were able to view the Hangout live on NASA’s YouTube channel and were invited to ask questions by uploading a video question to YouTube with the hashtag #askISS, as well as from followers on Google Plus or Twitter, who were able to ask a question in advance of or during the event using the hashtag #askNASA, or on NASA’s Facebook page.
-

NASA Long-Distance Google+ Hangout to Connect with Space Station
In a first for the agency, NASA hosted a Google+ Hangout live with the International Space Station on Feb. 22, 2013 from 10:30 a.m EST to 11:30 a.m. EST. Google+ Hangouts allow people to chat face-to-face while thousands more can tune in to watch the conversation live on Google+ or YouTube. This unique opportunity connected you, our fans, with astronauts living and working on the orbiting laboratory 240 miles above the Earth.
During the event, several video questions were selected and answered by astronauts on the space station and on the ground. Additionally, NASA asked real-time questions submitted by our followers on Google+, Twitter, and Facebook. During the hangout, astronauts Kevin Ford, Chris Hadfield and Tom Marshburn will answer questions and provide insights about life aboard the station. Station crews conduct a variety of science experiments and perform station maintenance during their six-month stay on the outpost. Their life aboard the station in near-weightlessness requires unique approaches to everyday activities such as eating, sleeping and exercising.
-

ESA Euronews: La forza di gravità terrestre
La gravità è una delle forze fondamentali della natura, con la sua presa invisibile governa tutto il nostro pianeta: dalle rocce, alle profondità dei mari. Per noi è un punto di riferimento vitale.
Normalmente percepiamo la gravità come un’attrazione costante ma, se si aggiunge della massa extra in un punto, o se la si toglie, il segnale gravitazionale si altera in modo misurabile, seppur minimo. E per la scienza è un rompicapo. La gravità può infatti variare in modi diversi. Può variare nel tempo, a causa dei movimenti della massa, e può variare da un posto all’altro.In questa puntata di Space siamo andati a Trieste, nel nord Italia, dove un gruppo di studenti è alle prese con la gravità. Sottoterra c’è una immensa caverna: la Grotta Gigante. Qui la forza di gravità si riduce sensibilmente il che significa che una massa minore sotto i nostri piedi corrisponde a un’attrazione inferiore verso la Terra.
Il nostro pianeta inoltre, se visto con gli occhi di un satellite in grado di scansionare la gravità, assume davvero una forma molto strana.
Per questo l’unico modo per avere un quadro globale del campo gravitazionale è andare nello spazio. Con questo obiettivo è nata la missione GOCE dell’Agenzia spaziale europea.
Un’opportunità relativamente nuova, quella di utilizzare satelliti per studiare la gravità. Fino al 1995 infatti il campo gravitazionale veniva studiato in alcuni centri come quello di Potzdam, in Germania, tramite pendoli ad alta precisione. -

ESA Euronews: El poder de la fuerza de la gravedad en la Tierra
La gravedad es una fuerza fundamental de la naturaleza, una fuerza invisible que domina nuestro planeta, desde sus entrañas rocosas a los océanos. Se trata de un fenómeno de atracción constante, estudiado hace siglos, pero que todavía arroja interrogantes a la comunidad científica. Si eliminamos o añadimo masa en un punto geográfico determinado, cambia la fuerza de la gravedad. Saber exactamente cuánto es complicado, porque varios factores influyen en el fenómeno gravitatorio.
La masa de los cuerpos es un factor determinante. En Trieste, Italia, un grupo de estudiantes indga sobre el fenómeno que Isaac Newton se planteó tres siglos atrás.. La premisa es intrigante. En esta zona hay una gran cueva, llamada Gruta Gigante. La ausencia de masa en el subsuelo reduce la fuerza de la gravedad en la zona. Es decir, si aparcamos un coche que pese una tonelada, aquí pesará cinco gramos menos. Pero la cueva no es el único factor involucrado, explica Carla Breitenburg, profesor de geofísica en la Universidad de Trieste. Un estudiante le preguntó por qué había cambios gravitacionales, si no habían cambiado de lugar en sus mediciones. La respuesta es porque la acción de la Luna y el Sol cambia el campo gravitacional. La forma de la Tierra se estire y encoge con el contínuo flujo de mareas.
La única manera de tener una percepción integral de este fenómeno es desde el espacio. Fue precisamente por esta razón que la Agencia Espacial Europea creó la misión GOCE. La información obtenida por este satélite puede desentrañar elementos importantes, como la presencia de hierro en el subsuelo. Según Carla Breitenburg “el espesor de la corteza puede variar entre 7 kilómetros debajo de los océanos, la zona donde es más delgada, y hasta 70, 75 millas en las zonas más montañosas, como los Andes o el Tíbet”.
Los datos que recoge el satélite GOCE, desde un centro de observación de la Agencia Espacial Europea en Roma, aporta cada vez más información a la comunidad científica. Un miembro del equipo, Bjoern Frommknecht explica que para conseguir mayor precisión del campo gravitatorio de la Tierra, el satélite GOCE vuela más bajo que nunca, “tan cerca como sea posible a la superficie exterior de la atmósfera”, aunque en esa órbita el aire sea un problema. GOCE siempre se mantiene a una altura inferior los satélites convencionales. Ahora pasará a los 268 kilómetros a los 237. Un objetivo importante es mejorar el modelo de geoide, la representación física de la gravedad de la Tierra. Otro es seguir el curso evolutivo del cambio climático, profundizando en lo que sucede debajo de la corteza terrestre.
Los satélites de la misión GRACE estudian precísamente la densidad del hielo en Groenlandia. La medición del geoide es también crucial en sectores complejos como la topografía y la navegación. -

ESA Euronews: Gravity’s grip on Earth
Gravity is one of the fundamental forces of nature, its invisible grip governing our planet – from the rocks inside to the seas on the surface.
In this edition of Space, we begin our adventure in a massive cave in northern Italy, a space beneath the surface of the Earth that is so big it has an effect on the local gravity field. If you parked a car weighing one tonne above this cave, it would weigh five grammes less than elsewhere.
However, getting a grip on gravity on a global scale can only be done from space, and that’s something ESA’s GOCE satellite mission has been doing since 2009. One of the ultimate goals of GOCE is to improve our knowledge of the geoid, a kind of ‘gravity map’ of the planet, that is essential for oceanographers, surveyors, engineers and Earth-science researchers.
Also tracking invaluable information about the Earth’s gravity field is the GRACE mission. While this pair of satellites don’t have the high precision of other missions, they offer something unique: a monthly survey of the gravity field. This US-German mission has been tracking the loss of ice mass over Greenland for the past decade, offering useful evidence for those studying climate change.
-

Marillion’s soundtrack for space
Rock band Marillion have a long-standing interest in science and exploration. In particular, guitarist Steve Rothery is fascinated by the images of Earth as seen from the International Space Station. He wrote a piece of music called “Space” some time ago and thought it would make a great accompaniment to video footage taken by astronauts on the Station.
Steve said, “I recorded this about ten years ago but it was never used. Today, my thought was to dedicate it to André Kuipers and all the space station crews past, present and future.”
Earlier, Marillion had sent a compilation of their songs up to the Space Station for ESA astronaut André Kuipers and the Expedition 30/31 crew.
Original music: ‘Space’ by S. Rothery/Marillion) Video previously published by M. König (images courtesy NASA/Image Science & Analysis Laboratory)
-

Stuck Like Glue – Sick Science! #128
Read the full experiment here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/content/experiment/stuck-like-glue-trick
A flame goes out inside of an upside down jar and, like magic, the jar is stuck to a plate. You might think that the jar has sucked right to the plate, but we’ll explain why this trick is actually a result of pushing!
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-
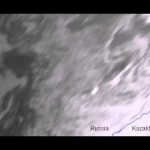
Satellite sees Russian meteor explosion from space
The meteor that exploded over the Urals of central Russia was seen by Eumetsat’s Meteosat-9, at the edge of the satellite view. Hundreds of people were reportedly injured as the meteor’s massive sonic boom caused widespread damage.
Credit: Eumetsat
-

“NASA Spinoff” Here!
The latest edition of NASA’s ” Spinoff” publication is out, highlighting some of the more than 1,800 products derived from NASA space technologies that touch nearly every aspect of our daily lives; from life-saving medical devices to the food we eat. Administrator Charlie Bolden explains why it’s part of NASA’s mission to ensure that the results of the agency’s research and development go on to benefit all of society. There’s more space in your life than you think! To learn more, visit us at spinoff.nasa.gov.
-

Balancing Act – Sick Science! #127
Find out why the rubber band makes it stronger here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment/balancing-act-cylinder-strength
If someone told you that they could balance a full-size text book on a piece of paper, you might call up the looney bin. That’s a crazy idea, right? Well, the notion that a book can sit, precariously, atop a plain piece of paper isn’t quite as bonkers as you might think!
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-

Navigating in space
ESA’s Flight Dynamics team uses cutting-edge computational techniques to plan, determine and control complex spacecraft trajectories. They apply fundamental physics and mathematics to 21st century spacecraft orbiting Earth and voyaging deep into our Solar System.
The Flight Dynamics team delivers precise orbital determinations enabling ground controllers to know where the spacecraft are located and prepare the manoeuvres to reach their targets like the Moon, Mars, Venus, a comet or a spacecraft constellation. The Flight Dynamics team also conducts mission analysis — they brainstorm about how robotic spacecraft can reach and return data from anywhere in the Solar System.
Flight dynamics scientists work as part of the team operating every ESA mission, whether in low-Earth orbit or soaring deep into our Solar System. They provide precise orbital calculations, determining where the spacecraft are located, which direction they’re facing, where they’re going and how far they’ve travelled.
This information is vital and is used every day not only by the mission controllers but also by supporting teams such as the Estrack station engineer, who have to know where to point their tracking antennas, what time to start ‘listening’ for a signal and how long a spacecraft will be visible.
-

Light Ice Heavy Water – Sick Science! #126
Find out the science behind Light Ice Heavy Water here http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/experiment/light-ice-cube-heavy-water
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
-

Steve Spangler Science Video Recap – January 2013
What a great start to 2013! From Pop Rocks, mystery liquids, folding eggs and even a VIRAL video showing how to remove iron from your breakfast cereal, to newspaper trees, dirty cell phones, and instantly freezing water. Hope you enjoyed this month as much as we did!
Don’t miss the season two premier of The Spangler Effect on March 6, 2013!
Want more experiments like this? Check out http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/product/naked-eggs-and-flying-potatoes
Sick Science™ is a trademark of Steve Spangler, inc.
© 2013 Steve Spangler Science all rights reserved
